
AlphaLISA Human TAU Detection Kit, 500 Assay Points
 View All
View All







The AlphaLISA™ Human Microtubule-associated Protein Tau (TAU) Detection Kit is designed for detection and quantitation of human TAU in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), buffered solution or cell culture medium in a homogeneous (no-wash steps, no separation steps) assay. The antibodies used in the kit correspond to clone numbers BT2 and Tau 12.
| Feature | Specification |
|---|---|
| Application | タンパク質定量 |
| Dynamic Range | 14.3 - 300,000 pg/mL |
| Limit of Detection | 14.3 pg/mL |
| Sample Volume | 5 µL |
The AlphaLISA™ Human Microtubule-associated Protein Tau (TAU) Detection Kit is designed for detection and quantitation of human TAU in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), buffered solution or cell culture medium in a homogeneous (no-wash steps, no separation steps) assay. The antibodies used in the kit correspond to clone numbers BT2 and Tau 12.















Product information
Overview
Formats:
- Our 500 assay point kit allows you to run 500 wells in 96-well or 384-well format, using a 50 µL reaction volume (5 µL of sample).
- Our 5,000 assay point kit allows you to run 5,000 wells in 96-well or 384-well format, using a 50 µL reaction volume (5 µL of sample).
Features:
- No-wash steps, no separation steps
- ELISA alternative technology
- Sensitive detection
- Broad sample compatibility
- Small sample volume
- Results in less than 3 hours
- Half the time of an ELISA assay
Microtubule-associated Protein Tau (TAU) is a neuronal protein that binds to axonal microtubules and has roles in the assembly of microtubules, cytoskeletal structure, and axonal transport. Six isoforms of Tau have been described, ranging from 352 to 441 residues, all originating from the alternative splicing of one gene designated MAPT. Tau interacts with tubulin to stabilize the microtubules, but its phosphorylation blocks this association, resulting in disruption of microtubule organization. In humans, hyperphosphorylated Tau can self-assemble into very insoluble aggregates (paired helical filaments) leading to various pathologies. Tauopathy is the name given to diseases associated with Tau accumulation, among which Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is one of the best known. Tau is a biochemical marker for this neurodegenerative disease as an increase of Tau in cerebrospinal fluid is observed in most patients with AD.
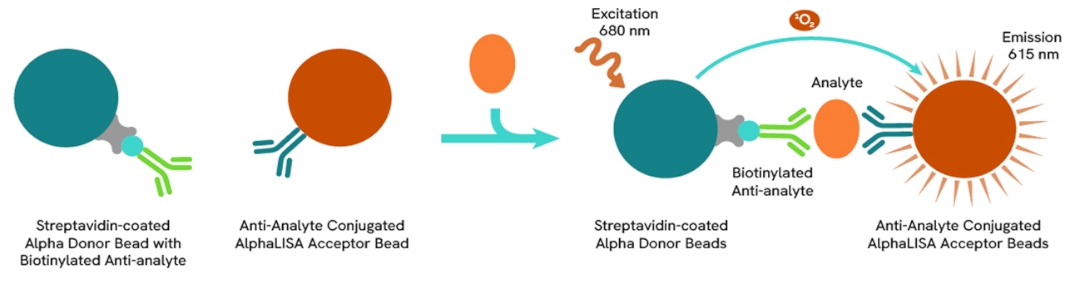
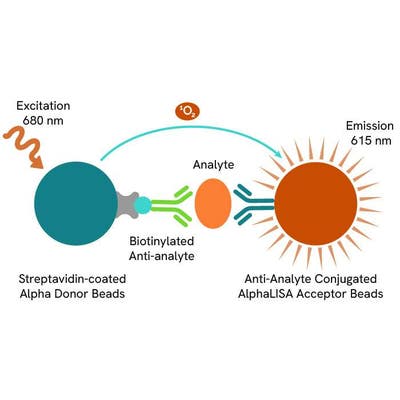
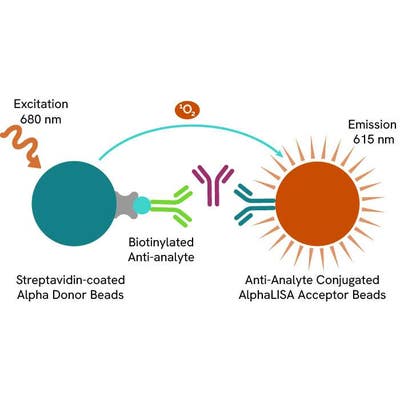
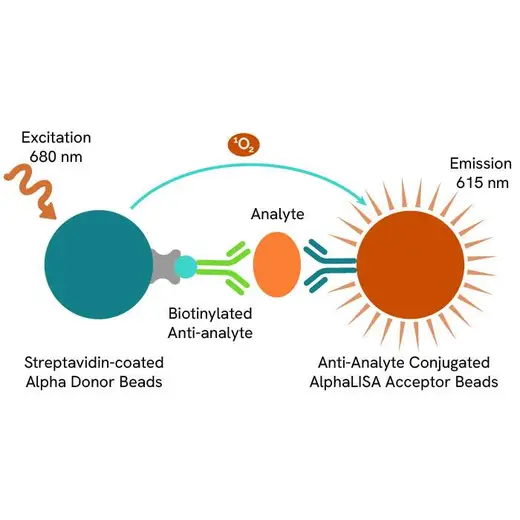
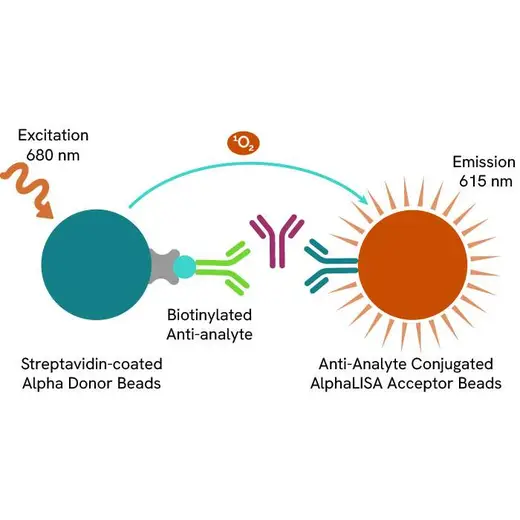
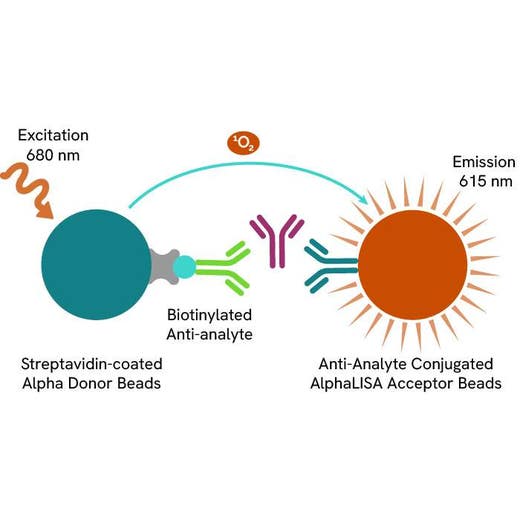
AlphaLISA technology allows the detection of molecules of interest in a no-wash, highly sensitive, quantitative assay. In an AlphaLISA assay, a biotinylated anti-analyte antibody binds to the Streptavidin-coated Donor beads while another anti-analyte antibody is conjugated to AlphaLISA Acceptor beads. In the presence of the analyte, the beads come into close proximity. The excitation of the Donor beads causes the release of singlet oxygen molecules that triggers a cascade of energy transfer in the Acceptor beads, resulting in a sharp peak of light emission at 615 nm.
How it works
Principle of the AlphaLISA assay
The AlphaLISA assay is based on an AlphaLISA sandwich immunoassay involving a biotinylated anti-analyte antibody bound to Streptavidin-coated AlphaLISA Donor beads and an anti-analyte antibody conjugated to AlphaLISA Acceptor beads. Both antibodies are directed against the analyte of interest. In the presence of the target, both antibodies bind to analyte and the beads come into proximity. The excitation of the Donor beads provokes the release of singlet oxygen molecules that triggers a cascade of energy transfer within the Acceptor beads, resulting in emission with λmax at 615 nm. The intensity of the signal is directly proportional to the concentration of analyte present in the sample.

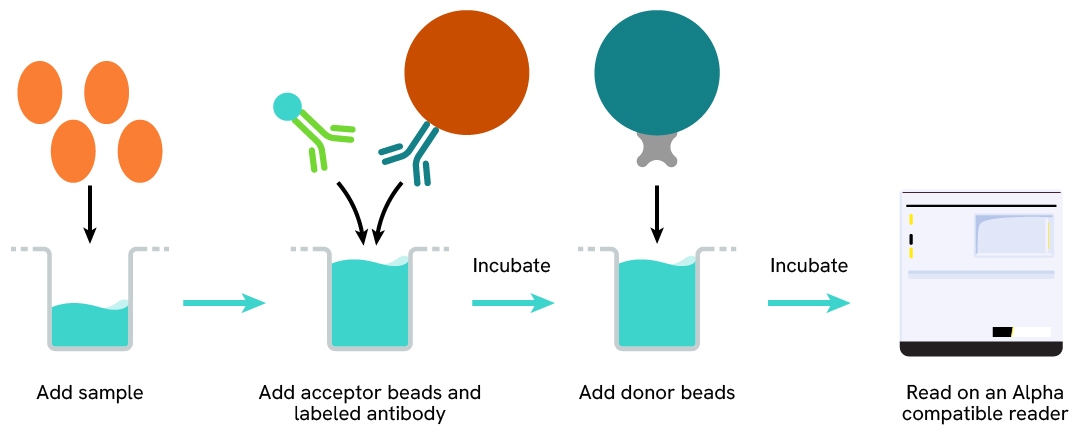
Protocol of the AlphaLISA assay
The AlphaLISA assay can be run in a 96- or 384-well detection plate (50 µL final). As described here, samples or standards are dispensed directly into the assay plate for the detection of the analyte of interest by AlphaLISA reagents. No washing steps are needed. The protocol can be further miniaturized or upscaled by simply resizing each addition volume proportionally.
Specifications
| Application |
Protein Quantification
|
|---|---|
| Automation Compatible |
Yes
|
| Brand |
AlphaLISA
|
| Detection Modality |
Alpha
|
| Dynamic Range |
14.3 - 300,000 pg/mL
|
| Limit of Detection |
14.3 pg/mL
|
| Product Group |
Kit
|
| Sample Volume |
5 µL
|
| Shipping Conditions |
Shipped in Blue Ice
|
| Target |
Tau
|
| Target Class |
Biomarkers
|
| Target Species |
Human
|
| Technology |
Alpha
|
| Therapeutic Area |
Central Nervous System
|
| Unit Size |
500 assay points
|
Video gallery
Resources
Are you looking for resources, click on the resource type to explore further.


How can we help you?
We are here to answer your questions.