In recent years, a discernable shift has taken place in the development of cancer therapeutics, marked by a growing emphasis on innovative drug delivery strategies. The focus has been on tailoring these strategies to enhance the precision of therapeutic targeting to tumor sites. Despite the undeniable success of conventional cancer treatment methods, they have several limitations. For example, challenges of chemotherapy include poor bioavailability, high-dose requirements, adverse side effects, and non-specific targeting.
To address this, targeted drug delivery systems have emerged with the primary aim of delivering therapeutic agents directly to cancer cells while minimizing damage to healthy cells. Various delivery methods are currently under exploration, including ligand or receptor-based targeting, triggered release mechanisms, intracellular drug targeting, gene delivery, cancer stem cell therapy, magnetic drug targeting, and ultrasound-mediated drug delivery. These treatments have the potential to enhance therapeutic effectiveness and possibly minimize systemically administered chemotherapeutic doses.
Despite the promise of targeted drug delivery strategies, there arises a pressing need for reliable and pre-validated methodologies to evaluate the effects of these delivery systems. Robust assessment tools are essential not only to accelerate the translation of these novel treatments from bench to bedside, but also to instill confidence in their safety and efficacy profiles.
In the development of new cancer therapeutics, researchers routinely assess the treatment’s influence on critical biological processes such as cell death. A widely employed approach for assessing cell death involves the use of annexin V probes. These molecular tools can identify apoptotic cells by binding to phosphatidylserine molecules exposed on the outer surface of these cells. Through the conjugation of annexin V with a fluorescent dye or other detectable labels, researchers can track and quantify apoptotic events using methods such as flow cytometry, fluorescence microscopy, or in vivo imaging.
Application in a therapeutic study
In a study conducted by UK-based researchers, annexin V probes were used to non-invasively assess apoptosis following the administration of novel MR-imageable thermosensitive liposomes (iTSL) in a triple-negative breast cancer murine model.1 These liposomes contained the chemotherapy agent doxorubicin and were equipped with focused ultrasound (FUS) triggerable release capabilities.
The study involved two cohorts of animals, with one receiving treatment with iTSL-DOX and an infusion of Revvity’s IVISense Annexin-V
 IVISense Annexin-V 750 Fluorescent Probe (Annexin-Vivo)
750 fluorescent probe 48 hours after treatment, and the other remaining untreated. Both groups received FUS targeting.
IVISense Annexin-V 750 Fluorescent Probe (Annexin-Vivo)
750 fluorescent probe 48 hours after treatment, and the other remaining untreated. Both groups received FUS targeting.
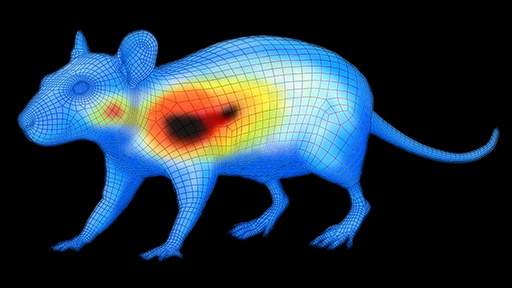
Using near-infrared fluorescence (NIRF) imaging to assess post-treatment apoptosis, the researchers found that the use of FUS targeting resulted in a significant increase in apoptosis within the treated tumor regions (Figure 1). This finding was further validated through histological analyses.
Conclusion
The findings from this study highlight the potential of combining advanced drug delivery systems with imaging techniques for real-time evaluation of treatment outcomes. The successful application of Revvity’s IVISense Annexin-V 750 fluorescent probes in visualizing apoptotic changes signifies a significant step forward in understanding the effects of novel anti-cancer treatments on cell viability. By integrating these probes into drug delivery studies, researchers can confidently assess and monitor therapeutic interventions, providing valuable insights into their efficacy and impact on cancer cell survival.
To help inform your decisions and drive your oncology research forward, we have developed an interactive Selector Guide for IVISense® fluorescent probes
 Guide
IVISense fluorescent probe selector guide for oncology research
for assessing growth, metabolism, protease activity, inflammation, cell death, hypoxia, and other important aspects of tumor biology.
Guide
IVISense fluorescent probe selector guide for oncology research
for assessing growth, metabolism, protease activity, inflammation, cell death, hypoxia, and other important aspects of tumor biology.
Reference
- Amrahli M, Centelles M, Cressey P, Prusevicius M, Gedroyc W, Xu XY, et al. MR-labelled liposomes and focused ultrasound for spatiotemporally controlled drug release in triple negative breast cancers in mice. Nanotheranostics. 2021;5(2):125–42. doi:10.7150/ntno.52168
For research use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
The information provided above is solely for informational and research purposes only. The information does not constitute medical advice and must not be used or interpreted as such. Consult a qualified veterinarian or researcher for specific guidance or use information. Revvity assumes no liability or responsibility for any injuries, losses, or damages resulting from the use or misuse of the provided information, and Revvity assumes no liability for any outcomes resulting from the use or misuse of any recommendations. The information is provided on an "as is" basis without warranties of any kind. Users are responsible for determining the suitability of any recommendations for the user’s particular research. Any recommendations provided by Revvity should not be considered a substitute for a user’s own professional judgment. Users are solely responsible for complying with all relevant laws, regulations, and institutional animal care and use committee (IACUC) guidelines in their use of the information provided.