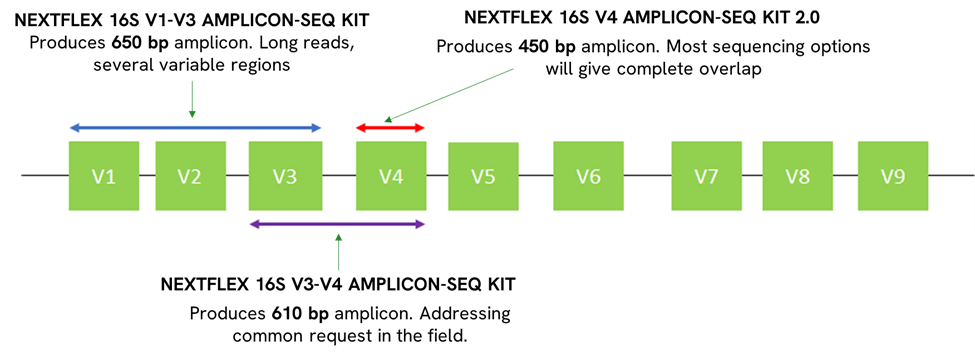
In the quest to understand the vast and diverse world of microorganisms, scientists have long sought methods that are both efficient and economical. Enter 16S metagenomics, a technique that has revolutionized our ability to characterize microbial communities. This powerful tool has provided a streamlined and cost-effective solution for researchers delving into the complexities of microbial life.
What is 16S metagenomics?
16S metagenomics refers to the sequencing of the 16S ribosomal RNA (rRNA) gene, a component of the prokaryotic ribosome that is highly conserved across bacterial species. This gene contains hypervariable regions that provide a unique fingerprint for identifying and classifying bacteria. By targeting this specific gene, scientists can obtain a snapshot of the microbial diversity within any given sample.
The streamlined process
The process of 16S metagenomics is straightforward. It begins with the extraction of DNA from a sample, followed by the amplification of the 16S rRNA gene using polymerase chain reaction (PCR). The PCR products are then sequenced, and bioinformatics tools are used to analyze the data, assigning taxonomic identities to the sequences obtained. This method bypasses the need for culturing microbes, which can be both time-consuming and often unfeasible, as many microorganisms are not readily culturable in the laboratory.
Cost-effectiveness
One of the most appealing aspects of 16S metagenomics is its cost-effectiveness. Traditional culturing methods can be expensive and often fail to capture the true diversity present in environmental samples. In contrast, 16S metagenomics allows for the analysis of thousands of sequences simultaneously, providing a comprehensive overview of microbial communities at a fraction of the cost.
Applications and future directions
The applications of 16S metagenomics are vast and varied. This technique has helped provided insights into the roles of. As sequencing technologies continue to advance and become more affordable, 16S metagenomics is poised to become even more accessible to researchers around the world.
Revvity has developed cutting-edge solutions for microbial sample processing and library preparation. It has also been working with leaders in the metagenomics space to make microbiome analysis accessible to all. Whether you’re an industry professional, an academic researcher, or a clinician, Revvity’s tools empower you to explore microbial ecosystems. We believe that democratization leads to breakthroughs.
In conclusion, 16S metagenomics stands as a testament to the power of modern molecular biology. It has provided a lens through which we can observe the previously unseen microbial world, offering a cost-effective and streamlined approach to understanding the intricate web of life that microbes weave.

For research use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
References:
- Bertolo, A., Valido, E., & Stoyanov, J. (2024). Optimized bacterial community characterization through full-length 16S rRNA gene sequencing utilizing MinION nanopore technology. BMC Microbiology, 24(1),58.
- Johnson, S. M., Carlson, E. L., & Xiang, Q. (2023). Enhancing taxonomic resolution in 16S metagenomics with dual-indexed, multiplexed sequencing. Journal of Microbiological Methods, 199(1), 105899.
- Patel, R. K., & Jain, M. (2021). NGS QC Toolkit: A toolkit for quality control of next generation sequencing data. PLOS ONE, 16(2), e0247409